Introduction Basal ganglia stuttering
Table of Contents
Stuttering can be a complex and challenging speech disorder that affects individuals of all ages. As we delve into the relationship between the basal ganglia and stuttering, it’s essential to grasp the significance of these brain structures and how they may influence the articulation process.
Understanding the Importance
For many people who stutter, the experience can feel isolating. You might relate to the frustration of trying to express thoughts only to find words stuck, creating a barrier between your thoughts and voice.
- Think of someone you know who faces challenges when speaking.
- Consider how everyday situations, like ordering coffee or participating in a meeting, can trigger anxiety.
By exploring the intricate connections within the brain, especially the role of the basal ganglia, we can uncover new insights that pave the way for better understanding and effective treatment of stuttering.

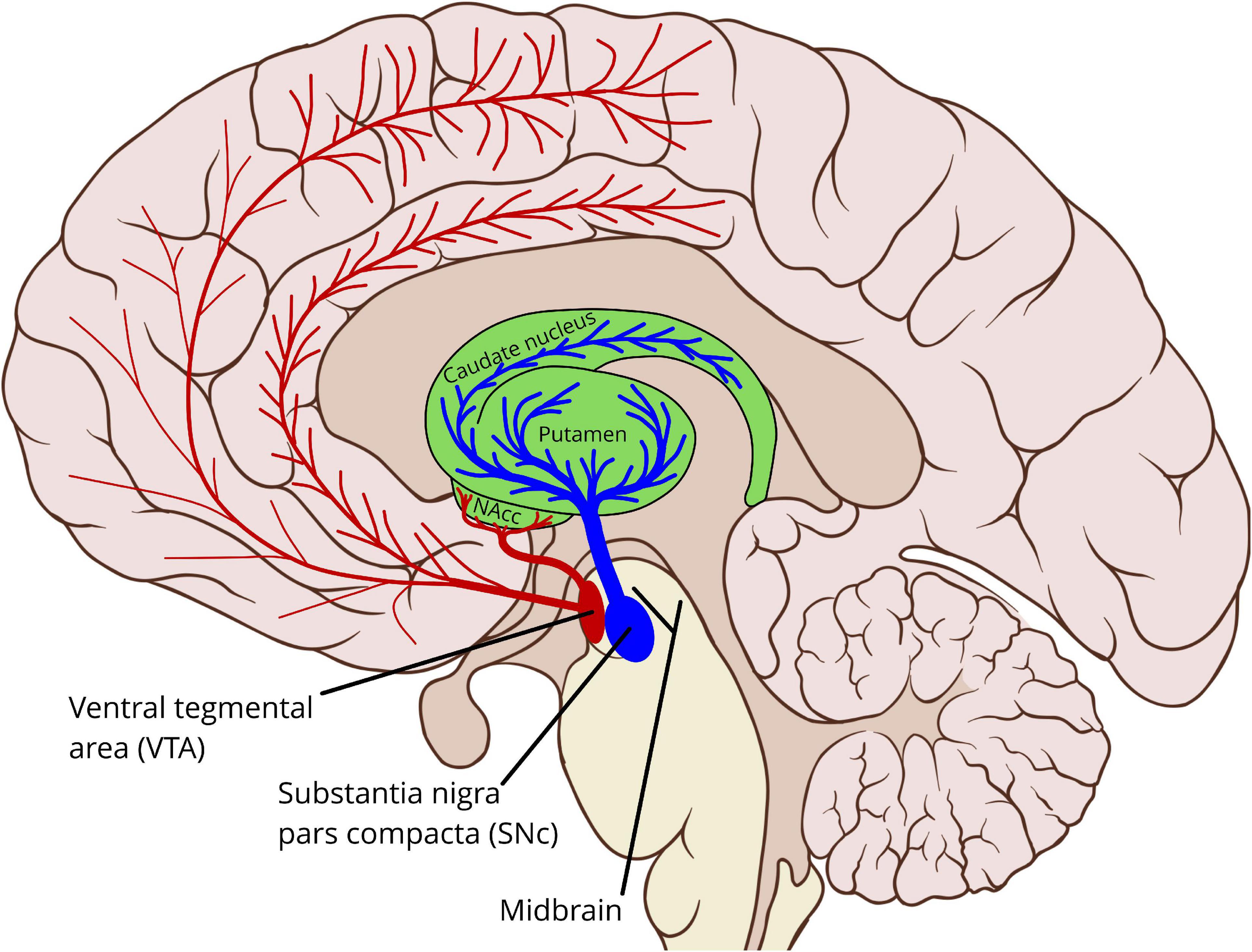
Understanding Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia play a pivotal role in how our brain functions, particularly in movement and coordination. They are a group of nuclei located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and are crucial for a range of activities beyond just motor control.
Functions of Basal Ganglia
These structures are involved in various functions that help streamline our daily movements and decision-making processes:
- Motor Control: They help initiate and regulate voluntary movements.
- Cognitive Functions: They also participate in learning, emotions, and attention.
- Habit Formation: The basal ganglia are essential for the development of habits, influencing how we perform routine tasks.
Thinking back to a time you began a new sport or hobby, you likely experienced that initial awkwardness before your movement became more fluid through practice. This improvement is partly thanks to the basal ganglia at work.
Role of Basal Ganglia in Motor Control
When it comes to motor control specifically, the basal ganglia:
- Select Movements: They help choose and initiate movements based on the context.
- Smooth Movements: They work to fine-tune and harmonize motions, ensuring actions are fluid.
- Prevent Unwanted Movements: By inhibiting unnecessary motions, they contribute to precise execution.
Imagine trying to pick up a glass of water. Your basal ganglia ensure that you don’t knock it over while smoothly bringing it to your lips. Their importance in these processes cannot be overstated, especially when considering how they may intersect with speech and conditions like stuttering.

Stuttering: Overview
While we’ve explored the complexities of the basal ganglia, it’s essential to shift our focus to stuttering itself. This speech disorder can significantly affect communication, shaping an individual’s social interactions and well-being.
Definition of Stuttering
Stuttering, also known as stammering, refers to a disruption in the flow of speech characterized by repetitions, prolongations, or blocks of sounds or syllables. It can be frustrating, often leading to feelings of anxiety during conversations.
- Common Symptoms:
- Repeating sounds or words (e.g., “I-I-I see you”).
- Stretching sounds (e.g., “Sssssometimes”).
- Inability to produce a word altogether (blocks).
Sharing a personal story can highlight its impact: imagine a friend who often avoids speaking up in class out of fear of stuttering, which affects their classroom participation.
Types of Stuttering
There are primarily two types of stuttering:
- Developmental Stuttering: Typically occurs in young children as they learn to speak. Most outgrow it, but some continue into adulthood.
- Neurogenic Stuttering: Often results from neurological conditions, such as strokes or brain injuries, affecting speech production.
Recognizing these distinct types can provide clarity and foster empathy in understanding those who stutter.

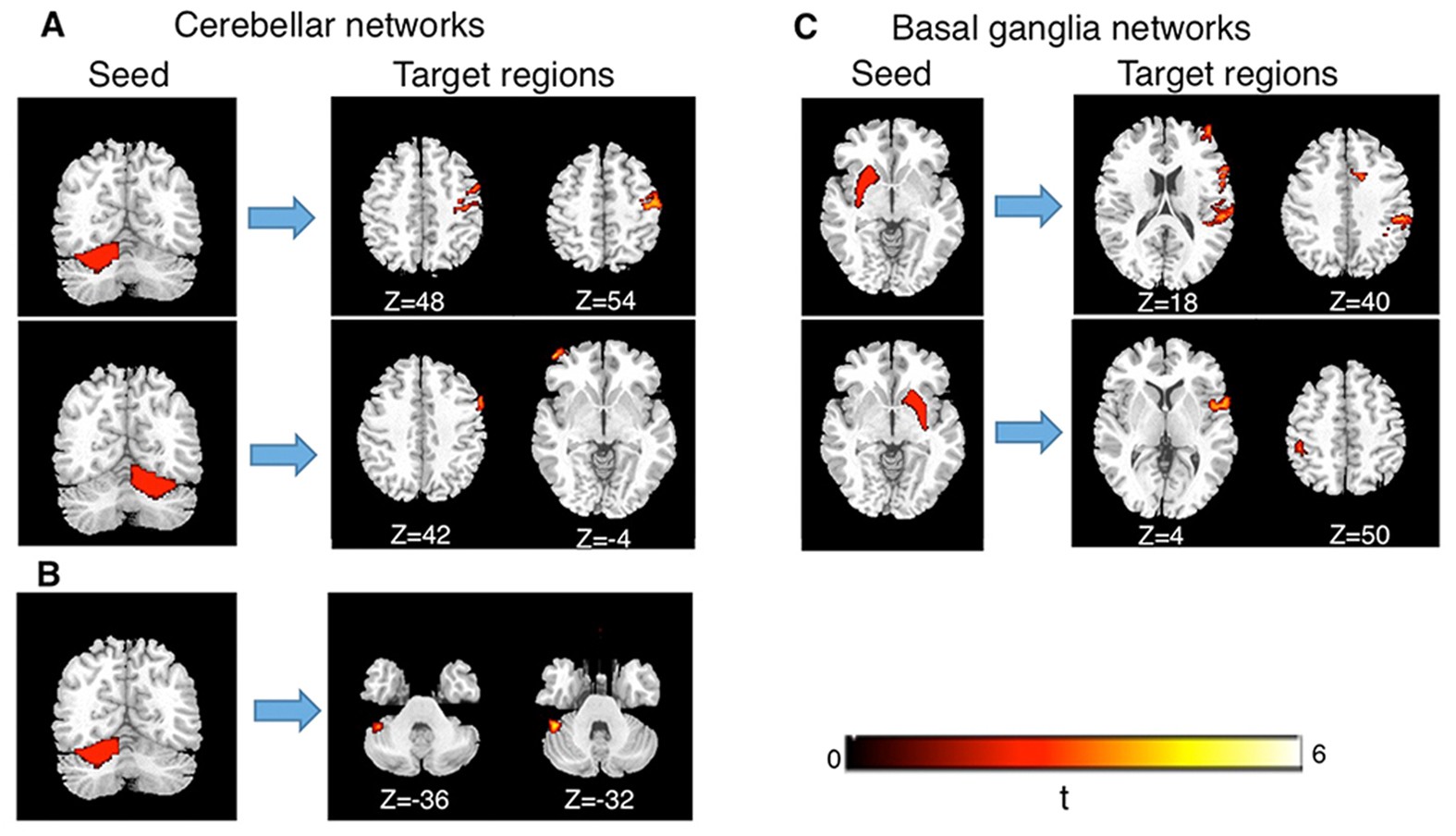
The Connection Between Basal Ganglia and Stuttering
As we dive deeper into understanding stuttering, it’s compelling to explore the link between the basal ganglia and this speech disorder. The intricate relationship between these brain structures and verbal communication underscores many therapeutic interventions.
How Basal Ganglia Influence Speech
The basal ganglia’s role in motor control extends to speech production, as they are responsible for the smooth execution of voluntary movements. When these functions are disrupted, it can lead to challenges in speaking.
- Dysregulation Impacts Speech: A dysfunction in the basal ganglia may contribute to the hesitations or blocks experienced during stuttering.
- Motor Planning and Coordination: The basal ganglia help coordinate the precise timing necessary for fluent speech.
Think about the moments when you’ve struggled to articulate your thoughts. Just as our physical movements can be clunky, speaking can falter when the basal ganglia’s processes aren’t functioning optimally. Understanding this connection opens new avenues for effective interventions and support for individuals who stutter.

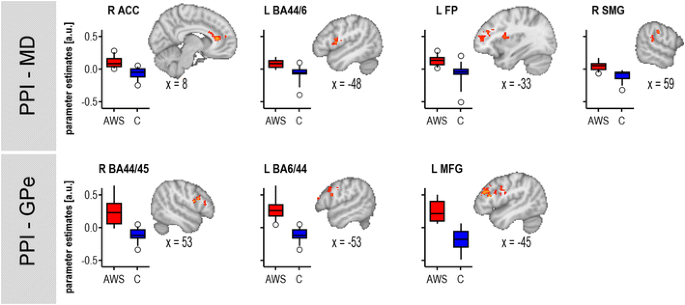
Research Findings on Basal Ganglia Involvement in Stuttering
Having established the connection between the basal ganglia and stuttering, it’s fascinating to look at the latest research findings that delve deeper into this relationship.
Insights from Recent Studies
Numerous studies have highlighted the basal ganglia’s involvement in stuttering, revealing intriguing insights:
- Brain Imaging Techniques: Advanced imaging, such as fMRI, has shown differences in the activation patterns of the basal ganglia in people who stutter compared to fluent speakers.
- Neurophysiological Considerations: Research indicates that disruptions in dopamine pathways, which often involve the basal ganglia, may contribute to stuttering symptoms.
Reflecting on these findings helps us understand why certain interventions, such as therapy that focuses on motor control, can be effective. Just as our physical capabilities are influenced by practice and training, so too can speech fluency improve as we address the specific neurology behind stuttering. This understanding is a step toward tailored therapies that meet the needs of those affected.
Treatment Options for Stuttering Related to Basal Ganglia
Armed with insights from research, we can explore effective treatment options for stuttering that are directly related to the functioning of the basal ganglia. Addressing the neurological aspects of this speech disorder offers new avenues for improvement.
Effective Treatment Approaches
Several strategies can help individuals manage their stuttering, particularly by focusing on the basal ganglia’s role:
- Speech Therapy: Tailored programs that incorporate motor control exercises can enhance fluency. Speech therapists often utilize techniques that improve coordination between thoughts and verbal expression.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of stuttering can alleviate anxiety and build confidence. CBT can help manage the fear of stuttering during social interactions.
- Neuroscience-Based Interventions: Innovative treatments employing technology, such as fluency-enhancing devices, are designed to engage the brain’s networks, including the basal ganglia.
Reflecting on the journeys of those who have found success can inspire many. Individuals often report that a combination of therapies not only improves their speech but also enhances their overall communication confidence.
Case Studies and Successful Interventions
With various treatment options available, examining case studies of successful interventions can provide valuable insights into effective strategies for managing stuttering.
Inspiring Examples of Success
Consider John, who struggled with severe stuttering throughout his childhood. After engaging in a comprehensive speech therapy program that emphasized motor control, he began seeing significant improvements. The therapy focused on:
- Breath Control Techniques: Helping him find his natural rhythm in speech.
- Gradual Exposure: Encouraging him to speak in progressively more challenging settings reduced his anxiety.
Another example is Sarah, whose stuttering was tied to emotional triggers. Through a combination of cognitive behavioral therapy and supportive group sessions, she developed coping strategies, enabling her to express herself with greater ease and confidence.
These stories demonstrate that success often lies in personalized approaches that target the unique aspects of each individual’s experience with stuttering, particularly through the lens of basal ganglia involvement.
Future Directions for Research on Basal Ganglia Stuttering Relationship
As we reflect on the successful interventions and the complex relationship between the basal ganglia and stuttering, the path forward in research presents exciting possibilities.
Emerging Areas of Focus
Future research can delve into several crucial areas to enhance our understanding and treatment of stuttering:
- Genetic Factors: Investigating hereditary components that might influence basal ganglia functionality related to stuttering could provide deeper insights.
- Integrative Approaches: Combining neuroscience with behavioral therapies may offer comprehensive methods to address the issue more holistically.
- Longitudinal Studies: Tracking individuals over time can help identify how interventions impact basal ganglia activity and, subsequently, speech fluency.
Just imagine the potential breakthroughs—new therapies could emerge, tailored specifically to improve the experience of people who stutter. As researchers continue to unravel these connections, the future looks promising for advancements that could lead to more effective treatments and support systems for those affected.